WARNING: Please Backup your registry before attemting this hack.Changes to registry may lead to system failure.
The following registry hack enables us to disable the Task Manager.
Step1: Goto start>run and type "regedit" in the run.
Step2: In the registry navigate to
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System
Value Name: DisableTaskMgr
Data Type: REG_DWORD (DWORD Value)
Value Data: (0 = default, 1 = disable Task Manager)
Step 3: Then navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System
Value Name: DisableTaskMgr
Data Type: REG_DWORD (DWORD Value)
Value Data: (0 = default, 1 = disable Task Manager)
Disable Task Manager
Advanced Google Search
Google is clearly the best general-purpose search engine on the Web.But most people don't use it to its best advantage. Do you just plug in a keyword or two and hope for the best? That may be the quickest way to search, but with more than 3 billion pages in Google's index, it's still a struggle to pare results to a manageable number.
But Google is an remarkably powerful tool that can ease and enhance your Internet exploration. Google's search options go beyond simple keywords, the Web, and even its own programmers. Let's look at some of Google's lesser-known options.
Syntax Search Tricks
Using a special syntax is a way to tell Google that you want to restrict your searches to certain elements or characteristics of Web pages.Here are some advanced operators that can help narrow down your search results.
1.Intitle: at the beginning of a query word or phrase (intitle:"Three Blind Mice") restricts your search results to just the titles of Web pages.
2.Intext: does the opposite of intitle:, searching only the body text, ignoring titles, links, and so forth. Intext: is perfect when what you're searching for might commonly appear in URLs. If you're looking for the term HTML, for example, and you don't want to get results such as
www.gohacking.com/index.html
you can enter intext:html
3.Link: lets you see which pages are linking to your Web page or to another page you're interested in. For example, try typing in
link:http://www.gohacking.com/
3.site: (which restricts results to top-level domains) with intitle: to find certain types of pages. For example, get scholarly pages about Mark Twain by searching for intitle:"Mark Twain"site:edu. Experiment with mixing various elements; you'll develop several strategies for finding the stuff you want more effectively. The site: command is very helpful as an alternative to the mediocre search engines built into many sites.
Swiss Army Google
Google has a number of services that can help you accomplish tasks you may never have thought to use Google for. For example, the new calculator feature
(www.google.com/help/features.html#calculator)
lets you do both math and a variety of conversions from the search box. For extra fun, try the query "Answer to life the universe and everything."
Suppose you want to contact someone and don't have his phone number handy. Google can help you with that, too. Just enter a name, city, and state. (The city is optional, but you must enter a state.) If a phone number matches the listing, you'll see it at the top of the search results along with a map link to the address. If you'd rather restrict your results, use rphonebook: for residential listings or bphonebook: for business listings. If you'd rather use a search form for business phone listings, try Yellow Search
(www.buzztoolbox.com/google/yellowsearch.shtml).
Let Google help you figure out whether you've got the right spelling—and the right word—for your search. Enter a misspelled word or phrase into the query box (try "thre blund mise") and Google may suggest a proper spelling. This doesn't always succeed; it works best when the word you're searching for can be found in a dictionary. Once you search for a properly spelled word, look at the results page, which repeats your query. (If you're searching for "three blind mice," underneath the search window will appear a statement such as Searched the web for "three blind mice.") You'll discover that you can click on each word in your search phrase and get a definition from a dictionary.
Extended Googling
Google offers several services that give you a head start in focusing your search. Google Groups
(http://groups.google.com/)
indexes literally millions of messages from decades of discussion on Usenet. Google even helps you with your shopping via two tools: FroogleCODE(http://froogle.google.com/),
which indexes products from online stores, and Google CatalogsCODE(http://catalogs.google.com/),
which features products from more 6,000 paper catalogs in a searchable index. And this only scratches the surface. You can get a complete list of Google's tools and services at
www.google.com/options/index.html
You're probably used to using Google in your browser. But have you ever thought of using Google outside your browser?
Google Alert
(http://www.googlealert.com/)
monitors your search terms and e-mails you information about new additions to Google's Web index. (Google Alert is not affiliated with Google; it uses Google's Web services API to perform its searches.) If you're more interested in news stories than general Web content, check out the beta version of Google News Alerts
(www.google.com/newsalerts).
This service (which is affiliated with Google) will monitor up to 50 news queries per e-mail address and send you information about news stories that match your query. (Hint: Use the intitle: and source: syntax elements with Google News to limit the number of alerts you get.)
Google on the telephone? Yup. This service is brought to you by the folks at Google Labs
(http://labs.google.com/),
a place for experimental Google ideas and features (which may come and go, so what's there at this writing might not be there when you decide to check it out). With Google Voice Search
(http://labs1.google.com/gvs.html),
you dial the Voice Search phone number, speak your keywords, and then click on the indicated link. Every time you say a new search term, the results page will refresh with your new query (you must have JavaScript enabled for this to work). Remember, this service is still in an experimental phase, so don't expect 100 percent success.
In 2002, Google released the Google API (application programming interface), a way for programmers to access Google's search engine results without violating the Google Terms of Service. A lot of people have created useful (and occasionally not-so-useful but interesting) applications not available from Google itself, such as Google Alert. For many applications, you'll need an API key, which is available free fromCODEwww.google.com/apis
SOURCE:http://www.pcmag.com/
Hacking Hotmail Password
These are some of the tricks that you can try to hack hotmail passwords.
Brute force hacking
a. Use telnet to connect to port 110 (Hotmail´s pop-server)
b. Type USER and then the victim´s username
c. Type PASS and then the guess a password
d. Repeat that until U have found the correct password.
!. This is called brute force hacking and requires patience.
It´s better than trying to guess the victims password on
hotmail homepage only because it´s faster.
The Best way
a. Get the username of the victim (It usually stands in the adress-field )
b. Then type " www.hotmail.com/cgi-bin/start/victimsusername "
c. U´re in!
!. This hack only work if U are on the same network or computer as the
victim and if he don´t log out.
The old way
a. Go to http://www.hotmail/proxy.html
b. Now type the victims username. (press login)
c. Look at the source code.
d. On the fifth row U should find "action=someadress"
e. Copy that adress and paste it into the adress-field
f. You are in...
!. As you can see it´s a long procedure and the victim have
plenty of time to log out.
Another...
a. Go to hotmail´s homepage
b. Copy the source code.
c. Make a new html file with the same code but change method=post to
method=enter
d. "view" the page
e. Change the adress to www.hotmail.com/ (don´t press enter!)
f. Make the victim type in his username and password
g. Look in the adress-field. There you´ll see ...&password:something...
!. This is the way I use, because it lets you know the password.
(If he exits the browser U can see the password in the History folder!)
MUST READ!
Hotmail´s system operators have changed the "system" so that the victim may logout even if U are inside his/her account. So don´t waste U´r time!
So you want to get some hotmail passwords?
This is pretty easy to do once you have got the hang of it. If you are a beginner, I wouldn't make this your first attempt at hacking. When you need to do is use a port surfer and surf over to port 80. While there, you have to try and mail the user that you want the password from.
It is best to mail them using the words
"We" and "Here at Hotmail..."
Most suckers fall for this and end up giving out their password. There is another way to also, you can get an anon mailer, and forge the addres as staff@hotmail.com. But you have to change the reply address to go to a different addres like user@host.com. The person that you are trying to get the pass from MUST respond to that letter for the mail to be forwarded to you. Have text like "Please reply to this letter with the subject "PASSWORD" and underneith please include your user name and password.
If you have trouble Loging in withing the next few days, this is only because we are updating our mail servers but no need to worry, your mail will still be there. Even though the server may be down for an hour. From the staff at Hotmail, Thank You."
Change The Title Of Yahoo Messenger
Here’s how you change the title text that appears at the top of the Messenger window. By default, this is “Yahoo! Messenger”, followed by your status. Simply edit the ymsgr.ini file, which you will find in the same folder as the Messenger program, in your Program Files folder. Locate the file and open it in Notepad. Then, at the end, add the following:
[APP TITLE]
caption=YOUR TEXT
Here, “YOUR TEXT” is whatever you want in the title bar. Save the file and close Messenger. When you restart it you will see your text in the title bar.
Email Tracking
One of most the frequently asked question is how to track an email back to the sender.That is how to determine the sender of the email? The most obvious answer is by looking at the "From:" line! But this does not work all the time since most of the spammers forge the email address or most of the spam that we get has a forged email address.This is also known as a spoofed email.Is it possible to send email from other's address?Yes it is possible to send email from anyone's name.Why not, you can send an email even from Bill Gate's Email ID.If you need a proof look here!
For more information on how to send a spoofed email refer this post.
OK now let's come back to the topic of email tracking.So how do you determine where a message actually came from?For that you have to understand how email messages are put together in order to backtrack an email message. SMTP is a text based protocol for transferring messages across the internet. A series of headers are placed in front of the data portion of the message. By examining the headers you can usually backtrack a message to the source network, sometimes the source host. A more detailed essay on reading email headers can be found .
If you are using Outlook or Outlook Express you can view the headers by right clicking on the message and selecting properties or options.
Below are listed the headers of an actual spam message.I have double spaced the headers to make them more readable.
Return-Path: <s359dyxtt@yahoo.com>
X-Original-To: sriki@example.com
Delivered-To: sriki@example.com
Received: from 12-218-172-108.client.mchsi.com (12-218-172-108.client.mchsi.com [12.218.172.108])by mailhost.example.com (Postfix) with SMTP id 1F9B8511C7for <sriki@example.com>; Sun, 16 Nov 2003 09:50:37 -0800 (PST)
Received: from (HELO 0udjou) [193.12.169.0] by 12-218-172-108.client.mchsi.com with ESMTP id <536806-74276>; Sun, 16 Nov 2003 19:42:31 +0200
Message-ID: <n5-l067n7z$46-z$-n@eo2.32574>
From: "Maricela Paulson" <s359dyxtt@yahoo.com>
Reply-To: "Maricela Paulson" <s359dyxtt@yahoo.com>
To: sriki@example.com
Subject: You Have won $10000 in US Lottery Scheme
Date: Sun, 16 Nov 2003 19:42:31 +0200
X-Mailer: Internet Mail Service (5.5.2650.21)
X-Priority: 3
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: multipart/alternative; boundary="MIMEStream=_0+211404_90873633350646_4032088448"
According to the From header this message is from Maricela Paulson at s359dyxxt@yahoo.com. I could just fire off a message to abuse@yahoo.com, but that would be waste of time. This message didn't come from yahoo's email service.
The header most likely to be useful in determining the actual source of an email message is the Received header. According to the top-most Received header this message was received from the host 12-218-172-108.client.mchsi.com with the ip address of 21.218.172.108 by my server mailhost.example.com. An important item to consider is at what point in the chain does the email system become untrusted? I consider anything beyond my own email server to be an unreliable source of information. Because this header was generated by my email server it is reasonable for me to accept it at face value.
The next Received header (which is chronologically the first) shows the remote email server accepting the message from the host 0udjou with the ip 193.12.169.0. Those of you who know anything about IP will realize that that is not a valid host IP address. In addition, any hostname that ends in client.mchsi.com is unlikely to be an authorized email server. This has every sign of being a cracked client system.
Here's is where we start digging. By default Windows is somewhat lacking in network diagnostic tools; however, you can use the tools at to do your own checking.
sriki@nqh9k:[/home/sriki] $whois 12.218.172.108 AT&T WorldNet Services ATT (NET-12-0-0-0-1)12.0.0.0 - 12.255.255.255Mediacom Communications Corp MEDIACOMCC-12-218-168-0-FLANDREAU-MN (NET-12-218-168-0-1)12.218.168.0 - 12.218.175.255
# ARIN WHOIS database, last updated 2003-12-31 19:15# Enter ? for additional hints on searching ARIN's WHOIS database.
I can also verify the hostname of the remote server by using nslookup, although in this particular instance, my email server has already provided both the IP address and the hostname.
sriki@nqh9k:[/home/sriki] $nslookup 12.218.172.108
Server: localhostAddress: 127.0.0.1
Name: 12-218-172-108.client.mchsi.comAddress: 12.218.172.108
Ok, whois shows that Mediacom Communications owns that netblock and nslookup confirms the address to hostname mapping of the remote server,12-218-172-108.client.mchsi.com. If I preface a www in front of the domain name portion and plug that into my web browser, http://www.mchsi.com/, I get Mediacom's web site.
There are few things more embarrassing to me than firing off an angry message to someone who is supposedly responsible for a problem, and being wrong. By double checking who owns the remote host's IP address using two different tools (whois and nslookup) I minimize the chance of making myself look like an idiot.
A quick glance at the web site and it appears they are an ISP. Now if I copy the entire message including the headers into a new email message and send it to abuse@mchsi.com with a short message explaining the situation, they may do something about it.
But what about Maricela Paulson? There really is no way to determine who sent a message, the best you can hope for is to find out what host sent it. Even in the case of a PGP signed messages there is no guarantee that one particular person actually pressed the send button. Obviously determining who the actual sender of an email message is much more involved than reading the From header. Hopefully this example may be of some use to other forum regulars.
Change IP Address
How to change your IP address in less than a minute? The following trick gives you a step-by-step procedure to change your IP address.
1. Click on "Start" in the bottom left hand corner of screen.
2. Click on "Run".
3. Type in "command" and hit ok.You should now be at an MSDOS prompt screen.
4. Type "ipconfig /release" just like that, and hit "enter".
5. Type "exit" and leave the prompt.
6. Right-click on "Network Places" or "My Network Places" on your desktop.
7. Click on "properties".
You should now be on a screen with something titled "Local Area Connection", or something close to that.
8. Right click on "Local Area Connection" and click "properties".
9. Double-click on the "Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)" from the list under the "General" tab.
10. Click on "Use the following IP address" under the "General" tab.
11. Create an IP address (It doesn't matter what it is. I just type 1 and 2 until i fill the area up).
12. Press "Tab" and it should automatically fill in the "Subnet Mask" section with default numbers.
13. Hit the "Ok" button here.
14. Hit the "Ok" button again.You should now be back to the "Local Area Connection" screen.
15. Right-click back on "Local Area Connection" and go to properties again.
16. Go back to the "TCP/IP" settings.
17. This time, select "Obtain an IP address automatically".
18. Hit "Ok".
19. Hit "Ok" again.
20. You now have a new IP address.
Some ISPs do not support this type of procedure and hence there are chances of getting back the same old IP address even after trying this hack.In this case you need to switch off the modem and then switch it on to get the new IP address.
NOTE: All these tricks works only if you have a dynamic IP address.But if you have a static IP address you have no option to change your IP.
How To Disable Windows Logo Key?
At times it becomes necessary to disable the Windows Key on the keyboard.For example when playing games this nasty Windows Logo key keeps annoying , as we often accidently press it and this takes our game out to the desktop.So it becomes necessary to disable it when not needed an re-enable it when needed.
The following download consists of two registry scripts (.reg) one to disable windows key and the other to re-enable it.In this download there are two files
disable_winlogo_key.reg - Disable Windows Logo Ley
re-enable_winlogo_key.reg - Re-Enable Windows Logo Key
DOWNLOAD
Windows XP IP Utilities
The following are the IP utilities available in Windows that help in finding out the information about IP Hosts and domains.These are the basic IP Hacking Commands that everyone must know!
NOTE: The term Host used in this article can also be assumed as a Website for simple understanding purpose.
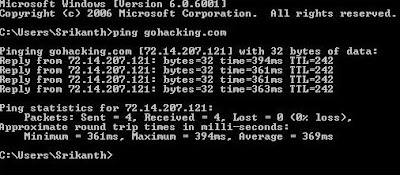
1. PING
PING is a simple application (command) used to determine whether a host is online and available.PING command sends one or more ICMP Echo messages to a specified host requesting a reply.The receiver (Target Host) responds to this ICMP Echo message and returns it back to the sender.This confirms that the Host is online and available.Otherwise the host is said to be unavailable.
Syntax:
C:\>ping gohacking.com
The following image shows the ping command which pings the host gohacking.com
2. TELNET
Telnet command is used to connect to a desired host on a specified port number.For example
Syntax:
C:\>telnet yahoo.com 25
C:\>telnet yahoo.com
NOTE: The default port number is 23.When the port number is not specified the default number is assumed.
Telnet Hacking is explained in detail in the following post.
How To Send Fake Email
3. NSLOOKUP
Many times we think about finding out the IP address of a given site.Say for example google.com,yahoo.com,microsoft.com etc.But how to do this? For this there are some websites that can be used to find out the IP address of a given site.But in Windows we have an inbuilt tool to do this job for us.It is nslookup.Yes this tool can be used for resolving a given domain name into it's IP address (determine the IP of a given site name).Not only this it can also be used for reverse IP lookup.That is if the IP address is given it determines the corresponding domain name for that IP address.
Syntax:
C:\>nslookup google.com
The following images shows the usage of nslookup command.
4. NETSTAT
The netstat command can be used to display the current TCP/IP network connections.For example the following netstat command displays all connections and their corresponding listening port numbers.
Eg: C:\>netstat -a
This command can be used to determine the IP address/Host names of all the applications connected to your computer.If a hacker is connected to your system even the hacker's IP is displayed.So the netstat command can be used to get an idea of all the active connections to a given system.










